Cheat sheet
Fundamentals
Software State
- Static : Test code for linting and style issues
- Dynamic : Test software functionality
Importance of software testing
- No straight forward process
- Depends on software requirements
- Objectives :
- prevents defects by evaluating requirements
- verifies requirements fulfillment
- verifies software behavior
- find defects
- comply with contract
- Tester roles :
- review requirements and prevent ambiguity in definition
- collaborate with dev to ensure requirements are understood and define tests
- detect errors and report software readiness
Error vs. Defect vs. Failure
- misunderstanding of a requirement , error -> invalid user story , defect -> wrong code, defect -> issues while running , failure
- error -> defect -> failure
code defects
- Lack of skills
- Communication problems
- Time pressure
- Absence of clear test procedure
Quality assurance QA vs Software testing
- Quality assurance, has as a process quality management, and within this quality management we can do software testing.
- Testing is part of QA
FP & FN
- False positive : Tests fails due to an error unrelated to software like Data ( badly structured data ... ) , environment ( Wrong java version ... )
- False negative : Test is not detecting existing defects
- Input + Preconditions => Output , Defect related to Preconditions are hard to detect and reproduce
Testing process and activities
Defect types
- Ambiguity : parts of the specs are not clear
- Inaccuracy : parts of the specs lack accuracy, too general or too free
- Inconsistency : parts of the specs clash with each other
TDD
Test driven development :
- Write unit tests before components and work to comply with those tests
Test levels
Components test
- Separate Unit / Module tests
- Objectives :
- verify module functionality
- prevent regression
- Assure component quality
- prevent defects from escaping to higher level ( Snowball effect )
- Objects ( Targets ):
- Class
- Module
- Function
- Data structure
- Detected defects :
- Incorrect logic
- Edge cases
Integration test
- focuses on data flow between components
- finds defect on interactions between system parts
System test
- Validates the complete and fully integrated software product
- Black box testing : The testing software has no idea what's inside the system
- Objectives :
- evaluate the end-to-end system specifications
- check compliance between input and outputs
Acceptance tests
- black box test
- performed by clients
- final phase
- validates businesses procedure
- as close as possible to production environment
Test process context
- Product risk
- Business domain
- operation constraints
- External / Internal policies
- SDLC : Software development lifecycle
- SDLC has a big impact of software testing
- Types :
- Sequential :
- Waterfall :
- Requirement analysis
- design
- coding
- testing
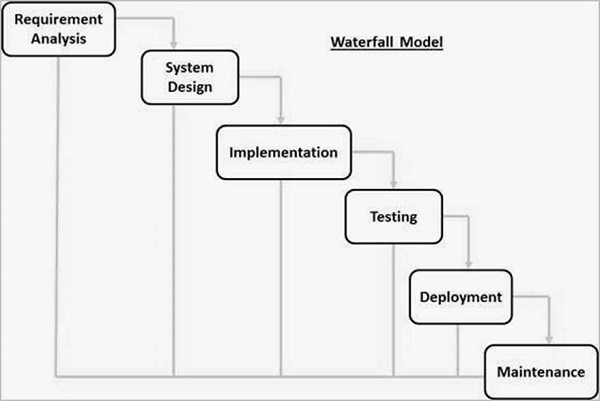
- V-Model : For every activity there's a test level
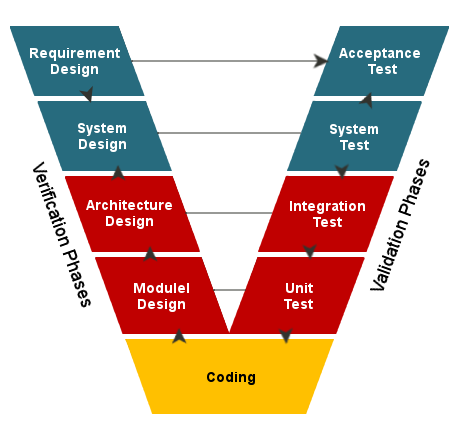
- Waterfall :
- Sequential :
- Iterative / Agile
- Incremental testing
- test activities overlap
- test targets / object have minor changes which catches defects faster
Test activities
Test planning
- Defines objectives
- Takes context into consideration
- Can be revisited after test monitoring
Test monitoring and control (always ongoing)
- monitoring : compares planned progress to actual progress
- control : take actions to meet objectives
- assert coverage criteria
- assert quality level
- determine the need for more tests
Test analysis (what to test)
- Identify what to stets
- Spec / implementation / system, analysis
- defect identification : ambiguity, Inaccuracy, Inconsistency
Test design (how to test)
- identify needed resources ( Vms , database ...)
- identify needed data
- design test environment
- design test cases
Test implementation (do we have everything in place in order to execute tests?)
- prepare test software (testware)
- Code tests
- Use test suites
- Build test env
Test execution
- Run tests : Automated / Manual
- Record test execution
- compare results with expected results
- Reports ( coverage, failed tests)
Test Completion
- Summery
- determine if changes are needed
- gather reports